Leading by Personalized Communication
October 17, 2024

Effective communication in a global economy requires us to be more human and less artificial. It is evidenced when Harvard Business Reviews' 10 Must-Reads on Change Management 2-Volume Collection (2021), includes “the 10 laws of human communication (Hugh Mackay, 1998)” to remind us to listen to each other more.
Answering the questions posed in the 7Cs model in global education provides insights into your ability to analyze and synthesize a global issue that is important to you based on factual evidence. Evidence-based insights furnish a global perspective into current practices of key stakeholders and their shared belief and value system that is important for community development.
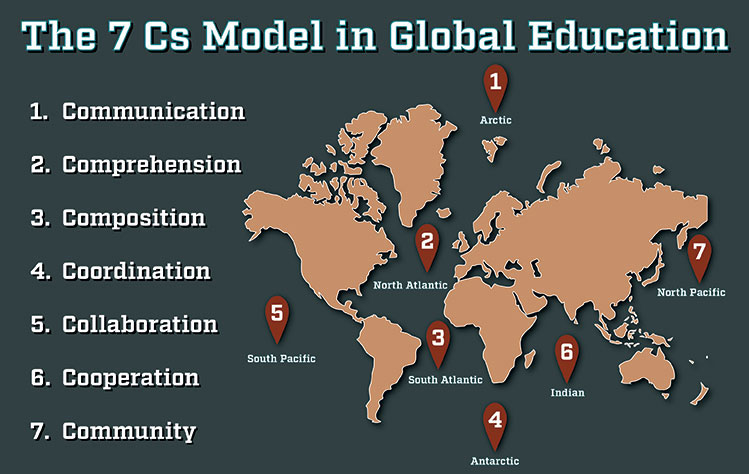
Image Transcript
The 7 Cs Model in Global Education makes a correlation between the seven seas of the world and the seven Cs in the global education model. The seven Cs consist of, communication, comprehension, composition, coordination, collaboration, cooperation and community.
In my opinion, successful communication encompasses our knowledge about the skills and practices required to make sense of the world in which we live. In addition, advanced digital technologies are changing so quickly, making it a challenge for us to interpret how things work virtually and in real life.
Leaders in the knowledge age understand the interconnectivity of the 7 Cs to affect a collective change required in the globalized world we live in today.
1. Communication. Communication involves two parties: the sender and the recipient. The sender intends to convey a message to a person or a group of people. The sender will achieve their intent to send the message only when the recipient understands the meaning of the message as intended by the sender.
With advanced information and communication technologies, communications are increasingly immediate, affording the sender and the recipient to exchange information and feedback as if they were physically in the same place. However, human communication is interpersonal. The process requires that both parties must listen for the meaning of the message and to ask to follow up questions in their responses to meet the purpose of this communication event at a moment in time.
How would you describe your ability to clearly convey the message when you engage in an ongoing exchange of information virtually online?
2. Comprehension. Comprehension is a learned skill, required the listeners/readers to decode the message as told by the communicator.
Advanced digital technologies afford people to virtually meet face-to-face online. This means both the sender and recipient must understand oral communications (spoken language) and textual communications in multiple media modes. Both parties use their ears and their eyes to process coded information to engage in a communication event in time. This also means that the recipient pays close attention to the meaning of the hidden message that can be buried in the audio and the video.
What approach do you use to make sense of these multimodal contents that you interact with online?
3. Composition. Composition refers to content produced by the author to tell a story as intended by the author. With access to digital tools and technologies, everyone is an author, telling stories from their perspectives. Gone are the days when big media corporations with sole ownership of different media channels and outlets acted as the gatekeepers of what stories should be presented and shared with the public.
Accessibility to tell our own stories assume that we are socially responsible citizens who will hold accountable for the accuracy of content.
How capable are you to use digital tools and technologies to make thoughtful content, share it with members of the community, and offer meaningful feedback?
4. Coordination. Coordination involves an act of passing information between and among all stakeholders for a smooth flow of information and activities to reach a mutual goal for all members in the community.
With advanced information and communication technologies, digital tools are facilitating these transactions in unchartered territories, resulting in both positive and negative impacts on members in the community.
How would you explain your capacity to facilitate the process of producing mutual benefits for all members?
5. Collaboration. Collaboration means working together to achieve a goal as agreed by members of the group. A collaborator is someone who values the power of teamwork, rather than a one-person show.
Digital tools make the quest to collaborate possible for everyone without geographic limitation. It is the first time in human history when we can join forces with like-minded people from different nations/cultures around the world for global equity and equality.
How would you explain your capacity to work with people from different beliefs and value systems with respect and an open mind?
6. Cooperation. Cooperation believes in community and shared leadership. Members of a cooperation value honesty, openness, social responsibility and caring for others. Consequently, cooperation leads from the middle instead of by command and control.
To cooperate means to put humans at the center of all the things we do. Through member participation and relations, cooperation brings in invaluable human capital and resources to benefit humanity.
How would you explain your capacity to wholeheartedly put others before yourself?
7. Community. Community refers to a group of people who share similar goals and dreams. Members of the community join forces and come together in the same place at the same time to connect with each other, creating a sense of belonging in the world in which they live.
Have you sought out to building a space to share common practices with other people?
Educational leaders in the information age use questions posed in this 7 Cs model to leading a meaningful conversation in global education.
Global education is an innovative mindset, focusing on collective thoughts and ways of thinking for a greater good. By upending the way that you think about personal growth and focusing on the unmet needs of others, you invert the priority of your own life. Equipped with a global perspective of how things operate online and in person, you lead a step change much needed in the world in which we live today.
